The UK financial system has been dogged by sluggish development for a very long time. Combined with even slower development in productiveness, it has meant just about no improve in dwelling requirements for the typical household over the previous decade.
Now the brand new chancellor, Kwasi Kwarteng, has unveiled what he says is a radical plan to get development again to its historic common of two.5% per yr. This can be a rise of a few proportion level, lifting dwelling requirements and offering extra money for public companies.
The central a part of Kwarteng’s mini price range includes reducing taxes within the hope of offering higher incentives for people and companies to work more durable and make investments extra, in what are the largest internet tax cuts from a chancellor for the reason that early Nineteen Seventies.
Much of this can profit the better-off greater than these on decrease incomes, however the authorities argues that increased development and never redistribution is the precedence, and that this can profit everybody because the financial pie turns into greater. So will this work?
Net tax cuts of UK chancellors
IFS
First, the highlights. The improve in nationwide insurance coverage is being cancelled, the very best fee of earnings tax and the cap on bankers’ bonuses abolished, and the essential fee of earnings tax reduce from 20% to 19% in April. Stamp responsibility on home purchases can also be being reduce, particularly for first-time patrons.
The hike in company tax scheduled for April won’t now go forward, whereas quite a lot of different incentives are being launched to stimulate funding and scale back the burden of regulation, together with decrease taxes for the self-employed. Added collectively, these measures will value £45 billion per yr.
In addition, the federal government is spending an enormous quantity to maintain power payments down. Moderating the deliberate rises for households will value an estimated £60 billion per yr for the subsequent two years, along with circa £30 billion to assist companies within the subsequent six months. The precise value will depend upon future gasoline costs.
Growth dividend?
The proof is inconclusive as as to whether decrease tax charges all the time incentivise people to work more durable and unleash their entrepreneurial spirit. In the UK, many could use the additional money to take pleasure in extra leisure time – notably with the variety of individuals within the workforce considerably lowered for the reason that pandemic, particularly these over 50.
Meanwhile, the truth that poorer individuals are set to realize comparatively little from the tax cuts could clarify why the federal government is planning to sanction those that work fewer than 15 hours per week and are usually not actively looking for jobs.
Ironically, within the wake of Brexit the federal government additionally sees elevated migration as a strategy to improve financial development by including extra staff to the financial system. However, rising the dimensions of the workforce doesn’t essentially increase productiveness (output per employee) – the important thing to increased incomes.
Most possible, the incentives for enterprise funding will due to this fact be essential to attaining any step-change in development, along with beforehand introduced plans to lift expertise.
UK GDP development 1949-2021
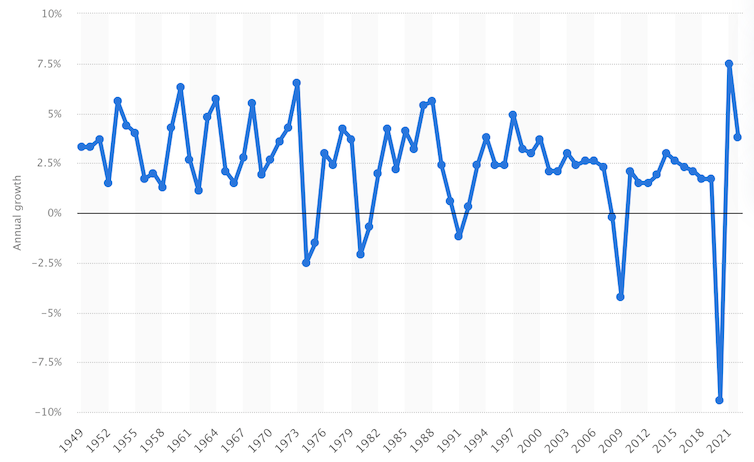
Statista
Business funding within the UK has been traditionally a lot decrease than that of its foremost rivals. However, successive cuts to company tax have made little distinction.
The identical goes for the various earlier schemes to incentivise particular investments, together with the Johnson authorities’s “super-deduction” for funding in plant and equipment.
With Kwarteng’s enterprise incentives additionally together with new low-tax funding zones and planning reform, it stays to be seen whether or not this can make a lot distinction. With a looming recession, excessive inflation, the power disaster, provide shortages and difficulties in recruiting expert staff, it’s onerous to envisage a dramatic shift within the quick time period.
The public funds
The authorities has recommended that if it succeeds in its goal of boosting annual development by one proportion level by 2026-27, there might be an additional £47 billion in tax revenues. This is a preliminary forecast which has not but been scrutinised by its Office for Budget Responsibility.
Yet within the quick time period, a giant squeeze on public spending is on the playing cards. The Institute for Fiscal Studies estimates that the impact of inflation shall be to chop departmental budgets in actual phrases by £18 billion in comparison with what was deliberate within the final spending assessment, and that’s earlier than public sector pay will increase.
The Treasury’s personal Growth Plan 2022 says that “holding spending below management” is a key a part of its dedication to fiscal accountability.
Regardless, the deliberate £90 billion in power subsidies and £45 billion in tax cuts will ship an infinite stimulus to the financial system. To curb the additional inflationary pressures that this can exert, the federal government shall be relying on the Bank of England to maintain elevating rates of interest sharply. But it isn’t clear how the stress between these two goals will play out.
Equally unsettling is the truth that the measures are set to lift the federal government’s deficit from £100 billion to just about £200 billion subsequent yr, or nearly 10% of GDP. This raises the prospect of UK authorities debt persevering with to rise as a proportion of GDP within the medium time period.
UK authorities debt as a % of GDP
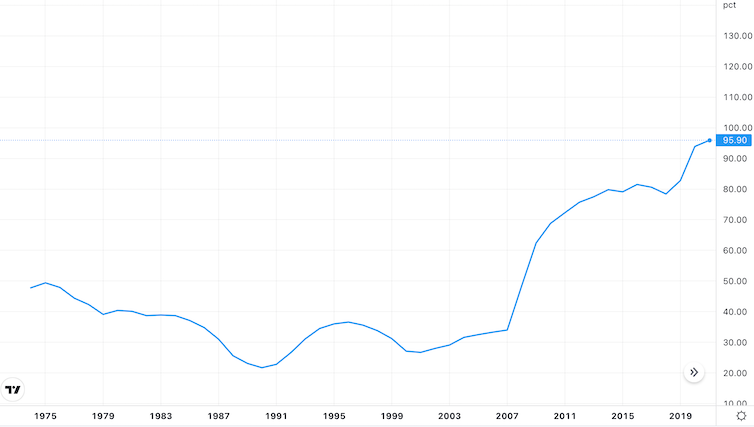
TradingView
The authorities argues that over 5 years, if its technique boosts development, it will add billions of kilos to tax revenues to service the debt, in addition to rising the general measurement of the financial system and due to this fact decreasing the debt-to-GDP fee. The markets have nonetheless reacted with concern, dumping UK authorities bonds and the pound after the announcement.
Where this leads
The authorities is obvious that its reforms will solely ship advantages over the medium time period. But short-term financial issues might derail the plan and threaten the probabilities of an election victory – most certainly as a result of be contested in 2024.
The mannequin of Liz Truss’s new authorities rehashes the technique of the Thatcher authorities within the Nineteen Eighties, the place tax cuts and deregulation arguably helped to spice up development. But tax charges had been a lot increased then, and the dimensions of the state industrial sector was a lot bigger.
Read extra:
Why Liz Truss isn’t any Margaret Thatcher in the case of the financial system
A extra worrying comparability, the place the “sprint for development” foundered over short-term financial issues, is perhaps the “Barber increase” launched by the 1970-74 Conservative authorities. An enormous financial stimulus led to hovering inflation, public sector pay strikes, and a overseas change disaster, resulting in the federal government’s defeat within the 1974 election.
This is a dramatic shift in authorities coverage that faces many obstacles. There might be a rocky street forward earlier than we see whether or not this gamble on development yields the end result that its proponents are promising.
![]()
Steve Schifferes doesn’t work for, seek the advice of, personal shares in or obtain funding from any firm or organisation that will profit from this text, and has disclosed no related affiliations past their educational appointment.
