Lego bricks have standardised elements and could be discovered internationally. Cardiff University, Author supplied
Sourcing human tissue samples for organic investigations isn’t all the time simple. While they’re ethically obtained by way of organ donation or from tissue that’s eliminated throughout surgical procedures, scientists are discovering them more and more tough to pay money for.
And it’s not simply because there’s a restricted provide of human tissue samples. There’s additionally restricted availability of the particular measurement and kind of tissue samples wanted for the numerous initiatives happening at any given time. That’s why we determined to handle the difficulty by constructing our personal low-cost, simply accessible printer able to creating human tissue samples utilizing one of many world’s hottest toys.
The emergence of 3D bioprinting has supplied a possible answer to the issue in sourcing tissue samples. This expertise entails loading “bio-ink”, which incorporates residing cells, right into a cartridge. That, in flip, is then loaded into the bioprinter. Once programmed, the bioprinter prints the cell-laden bio-ink to type 3D constructions that purpose to duplicate the complicated formation of organic tissue.
Unlike two-dimensional cell cultures grown on plates, which most of us nonetheless depend on for big elements of our analysis, bioprinters allow scientists to develop cells in three dimensions. And that higher replicates the intricate structure of human biology. In different phrases, bioprinting expertise permits researchers to make extra comparable fashions for learning wholesome and diseased tissue.
The drawback is that these machines come at an eye-wateringly excessive value of some tens, even a whole bunch, of hundreds of kilos. Few analysis groups, together with ours, can stretch their budgets to cowl that type of expenditure, irrespective of how groundbreaking the expertise guarantees to be.
That’s what led to us asking ourselves whether or not we might construct our personal inexpensive 3D bioprinter. The reply was “sure” and we determined to take action utilizing Lego.
Bored Photography/Shutterstock
Anyone who’s ever tinkered with it should know that not solely is Lego extraordinarily low cost and versatile, nevertheless it’s additionally manufactured to very excessive precision with standardised elements which can be globally accessible.
We additionally knew Lego had already been used to create conventional 3D printers. But what remained unsure was whether or not we might take the fundamental notion of a Lego 3D printer – which prints stable 3D constructions from plastic – and engineer one that might print comfortable organic materials.
The output would must be exact, dependable and steady for it to be of any use in our lab.
We started working on our personal inexpensive, high-spec bioprinter in a nook of our Cardiff lab utilizing normal Lego bricks, their mechanical sub-brand, Lego Mindstorms and a lab pump, which is a tool generally present in analysis labs. A multidisciplinary group of engineers and biologists labored collectively to design, engineer, assemble and program our bioprinter.
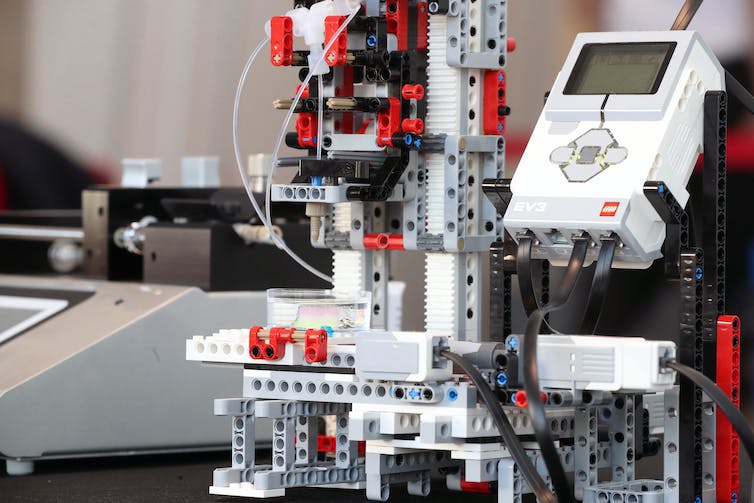
The 3D bioprinter is constructed from Lego and Lego Mindstorms.
Cardiff University, Author supplied
Still in its infancy, our bioprinter, which value £500 to construct, achieves the required stage of precision to supply delicate organic materials. The manner it does that is remarkably easy.
A nozzle ejects a gel-like substance, which is stuffed with cells, onto a dish. At the guts of the machine is a mini Lego Mindstorms laptop. This machine strikes the dish backwards and forwards and aspect to aspect whereas shifting the nozzle up and down mechanically because it extrudes the gel filled with cells. These programmable actions construct up layers of the cells to duplicate the 3D construction of human tissue, layer by layer.
Our bioprinter is now getting used to create layers of pores and skin cells, working in direction of a full-scale pores and skin mannequin. It may also be modified by utilizing several types of nozzles to print several types of cells, constructing quite a lot of complexities into the tissue samples. It’s an thrilling alternative to mimic each wholesome and diseased pores and skin, to take a look at present therapies and to design new therapies to deal with numerous pores and skin ailments.
The future
Our bioprinter couldn’t solely present us with an correct consultant mannequin of human pores and skin, it may be used so as to add diseased cells to the wholesome fashions we produce. This would allow us to review how pores and skin situations develop and the way wholesome and diseased cells work together. It would additionally allow us to see how pores and skin ailments progress and the way potential therapies could be developed.
Printing artificial human pores and skin utilizing a Lego 3D bioprinter.
We have supplied particulars on how we constructed our Lego 3D bioprinter, giving clear directions on the right way to reconstruct this machine in any lab, wherever on this planet. At a time when analysis funding is so squeezed, we’re providing an open supply, accessible and inexpensive various to a significant piece of kit that’s past most researchers’ budgets.
Quite merely, we would like our Lego bioprinter to allow researchers to conduct groundbreaking analysis as a result of that may in the end result in a greater understanding of biology and additional enhance human well being.
![]()
This work was funded by the British Skin Foundation. The article was drafted with Jo Blankley (Cardiff University).
This work was funded by the British Skin Foundation
